What does ABRSM Grade 5 Music Theory cover?
ABRSM Grade 5 Music Theory is a music theory examination by the Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music. It is also a prerequisite for taking grade 6 and above practical examinations.
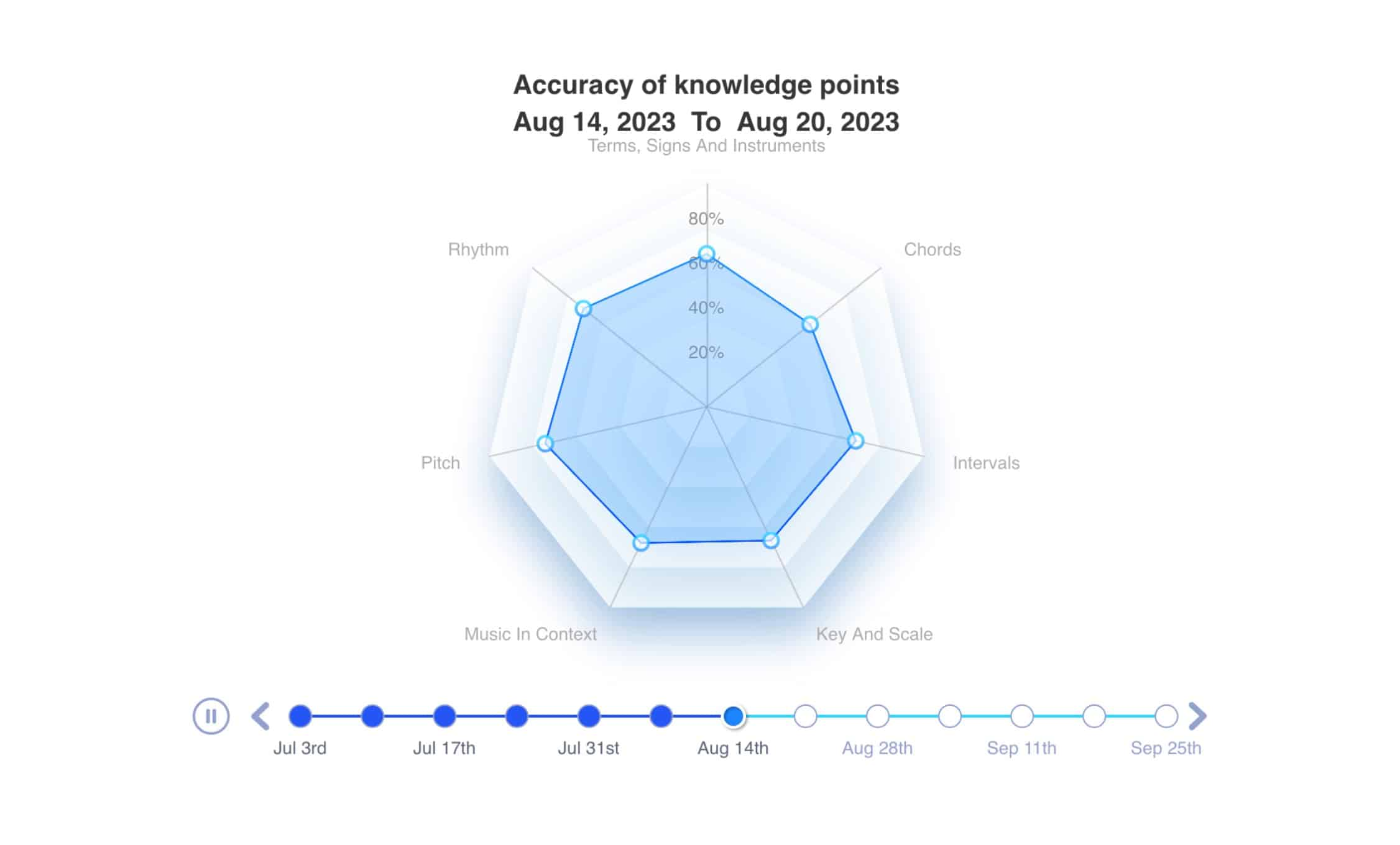
Seven Main Topics:
- Rhythm: Irregular time signatures, rests, note value completion, rhythmic groupings
- Pitch: Single intervals, note names, interval qualities, pitch comparison
- Keys & Scales: Key signatures, transposition, enharmonic equivalents, major and minor keys
- Intervals: Drag and drop interval questions, diminished intervals, augmented intervals
- Chords: Chord names, chord qualities, cadences
- Musical Terms, Signs & Instruments: Musical terminology, ornaments, instrumental knowledge
- Score Analysis: Comprehensive music score analysis ability
Exam Format:
- Number of Questions: 58 questions
- Exam Duration: 120 minutes
- Full Mark: 75 marks
- Pass Mark: 50 marks (66%)
- Merit: 60 marks (80%)
- Distinction: 65 marks (87%)
Preparation Tips:
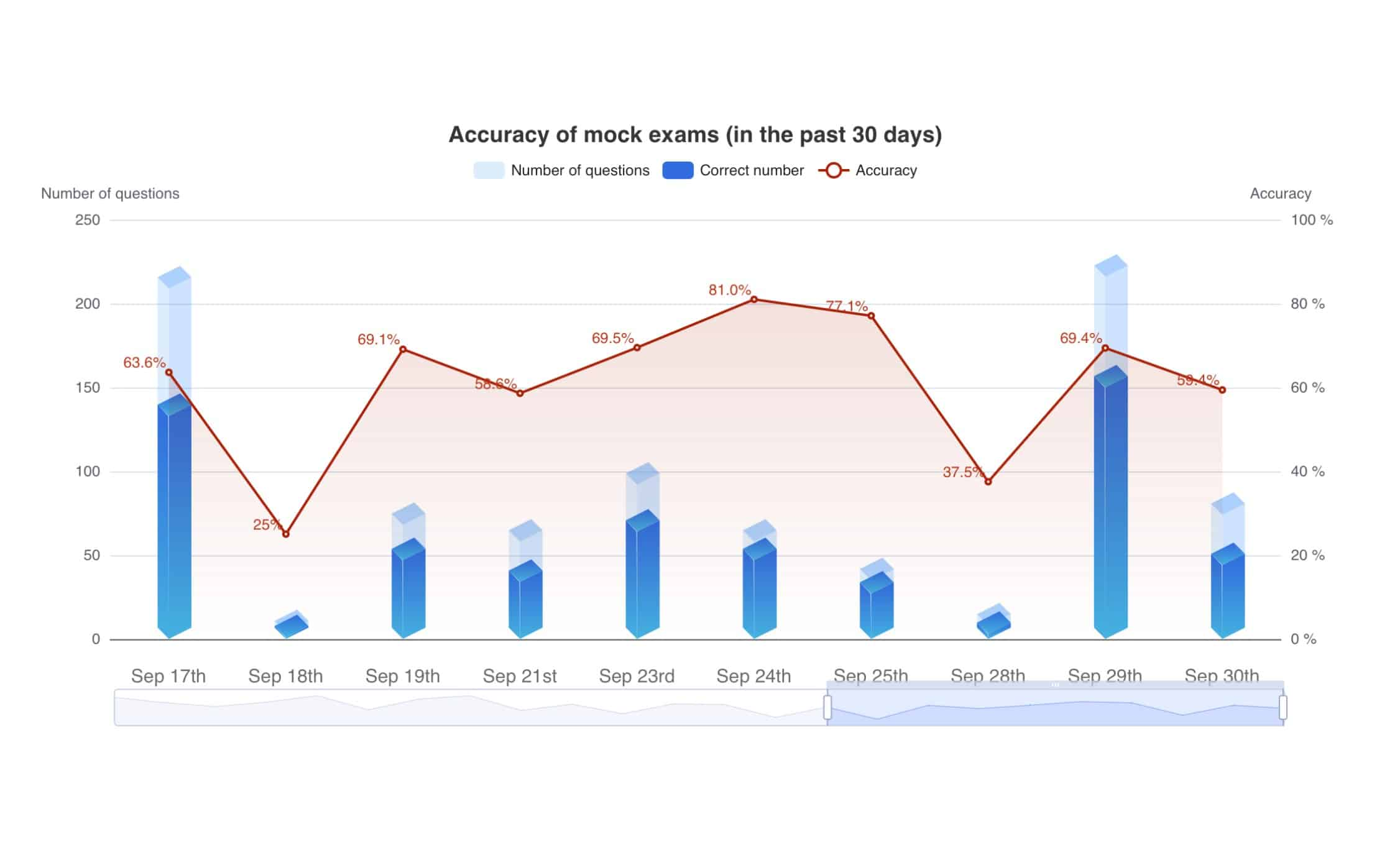
Use Music Theory Pro for systematic practice with 30 complete mock exam papers that faithfully replicate the official exam environment, and AI-powered question generation to strengthen weak areas.